In the series, here we are discussing on the Impacts of Coronavirus.
Political

- Many administrators from the Communist Party of China (CPC) were terminated due to their conduct on the quarantine situation in Central China. A sign of dissatisfaction with the political establishment’s reaction to the outbreak in those regions.
- The Italian government criticised the European Union’s absence of solidarity with coronavirus-affected Italy.
- The Iranian government has been brutally affected by the virus. On 14 March 2020, Iran’s President Hassan Rouhani wrote a public letter to world leaders pleading for help.
- The outbreak has provoked calls for the United States to acquire social strategies popular in other wealthy countries, comprising universal health care, universal child care, paid family leave, and higher levels of funding for public health.
- Diplomatic relations between Japan and South Korea deteriorated due to the pandemic, as South Korea criticised Japan’s “controversial and sluggish quarantine efforts”.
Educational

The educational impact of Coronavirus
As of 20 March, more than 960 million children and other students were impacted by interim or indefinite government-mandated school closures. Of these, 105 countries closed schools nationwide, implicating students who would generally attend pre-primary to upper-secondary classes, and 15 countries executed localized closures, impacting on an additional 640 million school children and other students.
On 18 March 2020, Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) released a statement announcing the postponement of ongoing Board Exams for Classes 10th and 12th across all countries.
In reaction to school closures, UNESCO suggested the practice of distance learning programs, open educational applications and strategies that schools and teachers can operate to reach pupils remotely and curb the upheaval of education.
Economical
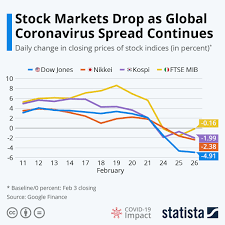
Coronavirus recession refers to an economic recession which may happen across the world economy in 2020.
Some economists suggest that China’s economy may contract for the first time since the 1970s. As the coronavirus spreads around the world, the stock markets have experienced their worst crash since 1987.
In India, there have been rumours regarding imposing financial emergencies. Approximately 53% of the businesses have been affected by the pandemic including all the major firms which are either cutting salaries of their employees or shutting off their operations completely.
Social
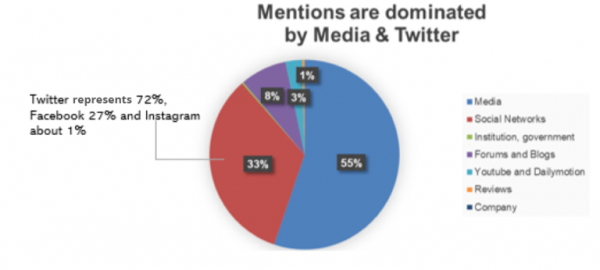
Social impact of Coronavirus on Social Media
While enormous progress has been made in responding to public health emergencies of COVID-19 disease and coordinating action internationally, much more needs to be done to better understand the repercussions of the measures taken on citizens and ensure their welfare.
Sentiments of people reflect fear and disgust towards the outbreak as their lives have come to a standstill and they are experiencing nothing but fear and disgust.
They are also in the awe that the COVID-19 outbreak might be an apocalypse they never expected of.
Environment

Due to the coronavirus outbreak’s impact on travel and industry, many regions underwent a drop in all kinds of pollution, such as:
- The Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air of China documented that techniques to restrict the spread of COVID-19, such as quarantines and travel bans, resulted in a 25% deduction of carbon emission in the country. In the first month of lockdowns, China generated approximately 200 million fewer metric tons of carbon dioxide due to the decrease in air traffic, oil refining, and coal consumption. It was computed that this decrease may have saved at least 77,000 lives.
- Between 1 January and 11 March 2020, the European Space Agency identified a marked deterioration in nitrous oxide emissions from cars, power plants and factories in the Po Valley region in northern Italy, occurring simultaneously with lockdowns in the region.
- In Venice, the water in the canals cleaned up and encountered an increased existence of fish and waterfowl.
Cultural

The cultural impact of Coronavirus shown by covering the statues by mask
Another contemporary and quickly stimulating aftermath of the infection is the cancellation of religious services, major tournaments in sports, the film industry, and other community-based events, such as music concerts, conferences, fashion shows and sports.
BCCI postponed IPL till 15th April resulting in resentment among the cricket fans of India and abroad. Even the filmmakers have postponed the release dates of their movies so that it doesn’t collide with the lockdown. All the major religious places such as mandirs, mosques, gurudwara, and churches have been closed down. Even the stand-up comic tours, concert tours, conferences, fashion shows have to be rescheduled or cancelled because of the outbreak.
Potential long-term impacts of COVID-19

Long term impact of Coronavirus
The political, cultural, and socio-economic impacts of the pandemic may concurrently cause crucial modifications in human civilization. Major intellectuals have indicated that this could comprise a boost in remote work, localization of international supply chains, and heightened political polarization.
Xenophobia and Racism

Xenophobia and Racism towards Chinese because if Coronavirus
Since the outbreak of COVID-19, exacerbated prejudice, xenophobia and racism have been reported towards people of European, Chinese and other East Asian origin, occurrences of fear, suspicion and hostility have been identified in many countries, especially in Europe, East Asia, North America and the Asia-Pacific region.
Some countries in Africa saw surging anti-Chinese sentiment as well. There has been supporting for the Chinese, both on and offline, towards those in virus-stricken areas, but many dwellers of Wuhan and Hubei have reported suffering discrimination based on their provincial lineage.
Since the succession of the outbreak to new hot-spot countries, people from Italy have also been subjected to scepticism and xenophobia.
This was all for this article, next we’d be talking about Myths Vs Facts in our article of COVID-19 Information Series.
Stay Tuned! Stay Safe! Stay Home!